In the age of big data, organizations are transforming their data management strategies. This data lakehouse architecture explores the multifaceted world of data lakehouses, their architecture, and how they amalgamate the features of data lakes and warehouses, alongside the associated technologies and practices that enhance data analytics and business intelligence.
Introduction to Data Lakehouse Architecture
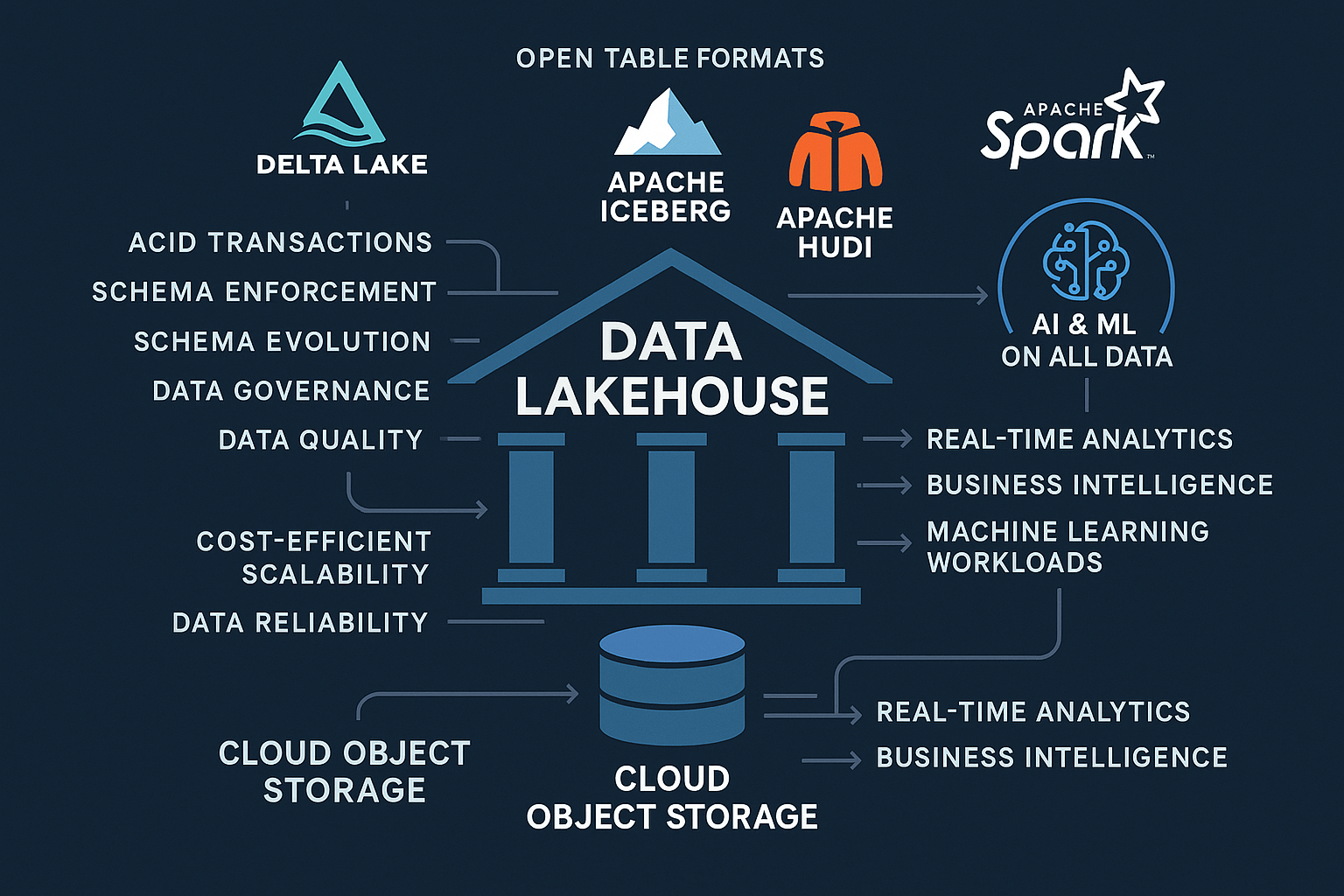
The data lakehouse architecture is a sophisticated blend that embodies the strengths of both data lakes and data warehouses, aimed at addressing the evolving demands of modern data management. At its core, a data lakehouse architecture consists of three primary layers: storage, processing, and analytics.
The storage layer utilizes cloud object storage, allowing for cost-effective scalability and flexibility. This layer accommodates various data formats, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, thereby supporting diverse use cases and data sources. By leveraging technologies like Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, and Apache Hudi, the data lakehouse architecture ensures ACID transactions and effective schema enforcement, which are critical for maintaining data integrity according to Databricks.
In the processing layer, tools such as Apache Spark facilitate data transformation and enrichment tasks. This layer is vital for unifying batch and streaming data, enabling real-time analytics to cope with the increasing demand for insights. The integration of these technologies allows organizations to perform complex analytics and machine learning workloads efficiently on all data generated across the enterprise, as outlined in Microsoft Research.
Finally, the analytics layer serves as an interface where business intelligence tools and data scientists can interact with the data. Here, various analytics processes can take place, from descriptive to predictive analytics. The unified data lakehouse architecture further enhances accessibility, breaking down silos and promoting collaboration across teams, ensuring that all stakeholders can derive value from data.
The entire data lakehouse architecture is designed to prioritize data quality and governance, allowing organizations to implement effective data governance frameworks while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This comprehensive architecture propels organizations toward achieving a cohesive data strategy, enabling them to extract actionable insights in an agile manner.
Understanding Data Lakehouse Architecture
Data lakehouse architecture combines the strengths of data lakes and data warehouses, creating a unified data platform that supports diverse data workloads. At its core, the architecture is typically segmented into three critical layers: storage, processing, and analytics.
The storage layer employs cost-efficient cloud object storage, which accommodates vast amounts of both structured and unstructured data. Unlike traditional data warehouses, which require predefined schemas, the lakehouse storage layer supports open table formats and allows for schema enforcement and evolution, enabling flexibility in data ingestion and adaptation. According to IBM, this adaptability is crucial for modern businesses.
The processing layer leverages advanced technologies such as Apache Spark to facilitate high-performance data transformation and processing, handling both batch and streaming data. This dual capability is pivotal for real-time analytics, allowing organizations to derive insights from fresh data as it becomes available.
In the analytics layer, the architecture provides seamless access to data for business intelligence, machine learning, and AI applications. By unifying data access across various data types and storage locations, the lakehouse structure allows for enhanced data governance and quality checks. ACID transactions ensure data reliability, preventing issues related to concurrent data processing and maintaining a consistent view of the data.
Moreover, the architecture supports an enterprise data strategy by integrating data mesh principles, granting decentralized data ownership while still centralizing necessary governance rules. This design not only empowers teams to innovate with machine learning workloads across all data types but also ensures that the data remains trustworthy and actionable for decision-making. Organizations benefit from a scalable solution that is adaptable to changing data needs, making the data lakehouse architecture an essential component of modern data architecture.
Key Technologies Behind Data Lakehouse Architecture
The landscape of data management is significantly enhanced by technologies like Databricks, Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, and Apache Hudi. These technologies form the backbone of lakehouse platforms, offering capabilities that bridge the gap between traditional data warehouses and modern data lakes.
One of the core features these technologies provide is support for ACID transactions, ensuring that data operations are reliable and consistent, even in high-demand environments. This transactional integrity is critical when managing data as it evolves, allowing organizations to easily roll back changes in case of errors, thus promoting data reliability.
Schema enforcement is another pivotal function, wherein data formats and structures are automatically validated upon ingestion. This guarantees that only clean, high-quality data is processed and stored, bolstering data governance practices across the board. Technologies like Delta Lake introduce robust schema evolution capabilities, empowering organizations to adapt to changing data requirements without sacrificing the integrity or availability of stored data.
Moreover, the capability for real-time analytics is a game-changer in today’s fast-paced data environments. With tools like Apache Spark integrated into lakehouse platforms, organizations can process both batch and streaming data seamlessly, enabling immediate insights and enhancing business intelligence applications as noted in a study by O’Reilly Media.
Ultimately, these technologies not only support the operational efficiency of lakehouse architectures but also enable organizations to implement a unified data architecture conducive to machine learning and AI applications. By providing cost-efficient scalability, they ensure organizations can effectively manage their data strategy in an evolving digital landscape.
The Dynamics of Data Lake vs. Warehouse vs. Lakehouse
Data lakes, data warehouses, and data lakehouses represent distinct approaches to data management, each with its own characteristics and use cases. Data lakes, characterized by their ability to store vast amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data, offer agility and scalability. Users can upload raw data without prior schema definition, accommodating various data types for advanced analytics and machine learning workloads. However, the lack of stringent governance often leads to challenges around data quality and reliability.
In contrast, data warehouses prioritize structured data storage and high-performance analytics. They enforce strict schemas and provide optimized queries for business intelligence tools. This makes data warehouses ideal for organizations needing consistent, reliable reporting based on historical data. However, the rigidity of schema enforcement presents limitations; data warehouse architectures can struggle with agile business demands, particularly in handling streaming data or accommodating rapidly evolving data schemas.
Data lakehouses emerge to bridge the gap between these two worlds, combining the flexibility of data lakes and the structured governance of data warehouses. Built on cloud object storage and leveraging technologies like Delta Lake or Apache Iceberg, lakehouses support ACID transactions, schema enforcement, and schema evolution. They enable real-time analytics and can handle both batch and streaming data efficiently. The lakehouse architecture supports a unified data platform that fosters data governance and quality, making it suitable for diverse use cases ranging from business intelligence to complex machine learning workloads.
In essence, selecting between data lakes, data warehouses, and lakehouses hinges on an organization’s specific data strategy. While data lakes serve exploratory needs, and data warehouses ensure high-performance analytics, data lakehouses provide a balanced approach, accommodating the unique demands of modern data architectures.
Real-time Analytics and the Role of Machine Learning in Data Lakehouse Architecture
Real-time analytics play a pivotal role in unlocking the value of data within data lakehouses, enabling organizations to gain immediate insights and respond dynamically to changing business conditions. Unlike traditional data architectures that may delay data processing and analysis, a lakehouse’s capabilities allow for seamless ingestion and processing of both batch and streaming data, creating a continuous flow of information. This advantage is crucial for businesses that require timely decision-making driven by live data.
The integration of machine learning workloads is integral to maximizing the potential of real-time analytics. Tools such as Apache Spark facilitate this integration, providing a unified framework for processing large volumes of data across various environments. With Spark’s capability to handle complex computations at speed, organizations can apply machine learning algorithms directly to streaming data, enabling predictive analytics and proactive responses. This empowers businesses to optimize operations, personalize customer experiences, and innovate processes based on real-time insights.
Furthermore, the use of open table formats like Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, and Apache Hudi allows for effective management of data lakes’ evolving schemas while supporting ACID transactions. This ensures data reliability and quality, which are essential when deriving insights from real-time data. The cost-efficient scalability of lakehouse platforms also supports extensive machine learning workloads, allowing organizations to leverage AI/ML tools on all their data, whether structured or unstructured, thereby enhancing their analytical capabilities.
By acting as a conduit for immediate analytics and advanced machine learning, data lakehouses empower businesses to navigate complex market dynamics and leverage insights that drive strategic initiatives, ultimately transforming data into a strategic asset.
Ensuring Data Quality and Governance in Data Lakehouse Architecture
Ensuring data quality and governance within a data lakehouse is vital for maximizing the benefits of modern data architectures. A comprehensive data governance framework helps organizations maintain control over data assets, ensuring accuracy, accessibility, and compliance. Key practices include schema evolution and metadata management, which facilitate adaptability in a landscape characterized by rapid changes in data types and sources.
Schema enforcement is critical to enforcing data quality; it ensures that only valid data enters the system. A strong governance model defines clear rules and standards for data entry, facilitating the adoption of ACID transactions. This means that all data operations are processed reliably, which enhances data consistency across various applications, including real-time analytics and machine learning workloads.
Metadata management serves as a cornerstone for effective data governance. It provides context for the data stored, making it easier to track lineage and understand data transformations. This transparency is crucial when integrating tools like Apache Spark, as it assures data scientists and analysts that they are working with high-quality, trustworthy information.
Furthermore, data quality assurance strategies involve regular audits and checks to identify anomalies or inconsistencies within the data lakehouse. Establishing these protocols operates synergistically with open table formats like Delta Lake and Apache Iceberg, which offer powerful mechanisms for maintaining data integrity, as emphasized in various studies available through TechRepublic.
By prioritizing these governance practices, organizations can harness the full potential of their data lakehouses while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and contributing to a robust enterprise data strategy. This foundation lays the groundwork for effective business intelligence and the deployment of AI and ML across all data environments.
Cost-effective Scalability and Data Reliability in Data Lakehouse Architecture
Cost-effective scalability is a defining characteristic of data lakehouses that sets them apart from traditional data architectures. As organizations grapple with rapidly growing volumes of data, the flexibility and efficiency of a lakehouse architecture become vital. Utilizing cloud object storage, lakehouses can leverage virtually limitless storage capabilities without the significant financial burden associated with provisioning dedicated data warehouse clusters. This allows enterprises to manage large datasets while keeping costs manageable, as the pay-as-you-go model facilitates cost-effective scalability according to actual usage.
Data reliability is prioritized through advanced technologies like ACID transactions, ensuring that even as data scales, integrity and consistency are maintained. The implementation of schema enforcement and schema evolution capabilities further assists in mitigating risks associated with data anomalies, as it allows datasets to adapt to changing organizational needs without compromising on quality. Additionally, the use of open table formats such as Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, and Apache Hudi enhances performance by offering features like time travel and versioning, which are crucial for maintaining reliable data over its lifecycle.
By supporting both batch and streaming data, lakehouses enable organizations to conduct real-time analytics, thus facilitating timely decision-making based on accurate and reliable data. This architectural approach empowers businesses to seamlessly integrate large-scale machine learning workloads while ensuring data reliability, ultimately enhancing the overall analytics capabilities. As organizations continue to expand their data operations, embracing the scalable and reliable nature of lakehouses fosters a robust framework for handling complex analytical demands efficiently.
Implementing an Enterprise Data Strategy with Data Lakehouse Architecture
Implementing an enterprise data strategy requires careful consideration of how data lakehouses can enhance an organization’s analytical capabilities and overall data management. As companies transition from traditional data architectures, they should embrace the flexibility and robustness offered by data lakehouse platforms. By integrating features of both data lakes and warehouses, these platforms provide a unified architecture that facilitates diverse data types, including batch and streaming data, catering to varying analytical needs.
Data mesh concepts can significantly augment this strategy, promoting distributed data ownership and accountabilities among different organizational teams. By enabling teams to manage and consume data as a product, organizations can foster a culture of collaboration and innovation while maintaining high standards in data governance and quality. The intrinsic capabilities of lakehouses, such as ACID transactions, schema enforcement, and schema evolution, reinforce the principles of data mesh, ensuring that data remain reliable, consistent, and easily accessible.
When implementing a lakehouse, it is crucial to leverage the power of modern technologies like Apache Spark, Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, and Apache Hudi, which support open table formats and allow seamless integration with cloud object storage. This enables organizations to harness real-time analytics and machine learning workloads efficiently, supporting a diverse range of business intelligence applications. Moreover, the cost-efficient scalability of data lakehouses ensures that enterprises can grow their data infrastructures in response to evolving demands, making it easier to derive insights from all available data. By strategically aligning lakehouse capabilities with their data mesh approach, organizations can enhance their enterprise data strategies, achieving a more agile and effective data management environment.
Conclusions on Data Lakehouse Architecture
Data lakehouses represent an innovative evolution in data architecture, combining the strengths of both data lakes and warehouses. As organizations increasingly rely on real-time data for decision-making, understanding and implementing lakehouse principles will be essential for maintaining data quality, governance, and scalability in a rapidly changing digital landscape.